Posted by admin on April 26, 2018
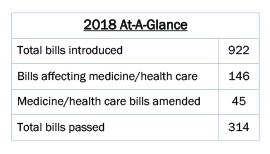
2018 Recap of the Regular Session of the Alabama Legislature
In times of illness, injury and emergency, patients depend on their physicians. But what if no one was on call? Public health would be in jeopardy. However, the same holds true for the Legislature. During the 2018 session alone, if the Medical Association had not been on call advocating for you and your patients, unnecessary and costly standards of care would have been written into law, lawsuit opportunities against physicians would have increased and poorly thought out “solutions” to the drug abuse epidemic ─ that could’ve made the problem worse ─ would have become law. Keep reading to find out more.
Moving Medicine Forward
The 2018 Legislative Session is over, but continued success in the legislative arena takes constant vigilance. Click here to download our 2018 Agenda.
If no one was on call…increased state funding for upgrading the Prescription Drug Monitoring Program (PDMP) would not have occurred. Working with the Governor’s Opioid Task Force, the Medical Association proposed increased funding for the PDMP, to allow it to be an effective tool for physicians. As a result, the Task Force made the request its number one recommendation to the Governor and the 2019 budget for the Alabama Department of Public Health (the PDMP administrator) has a $1 million increase for making a long-overdue upgrade to the user-friendliness of the drug database.
If no one was on call…legislation helping veterans at-risk for drug abuse get the care they need and also leverage technology to combat the drug abuse epidemic would not have occurred. Through enactment of SB 200, the prescription information of VA patients will be shared between the VA and non-VA physicians and pharmacists who are outside the VA system, the same kind of information sharing of prescription data that exists for almost all other patients. Passage of SB 200 also establishes a mechanism for vetting requests for release of completely de-identified PDMP information that can be used to spot drug abuse trends and help state officials better allocate resources in combatting this epidemic. The proposals that resulted in the drafting of SB 200 originated with a recommendation from the Governor’s Opioid Task Force, one the Medical Association supported.
If no one was on call…the concerns of physicians regarding the current state of affairs surrounding the Maintenance of Certification program would not have been heard. A formal recommendation from the Medical Association’s MOC Study Committee resulted in the enactment of SJR 62 by Senators Tim Melson, M.D., Larry Stutts, M.D., and the entire Alabama Senate. The resolution was signed by Gov. Kay Ivey. SJR 62 vocalizes Alabama physicians’ frustrations with MOC and urges the American Board of Medical Specialties to honor its commitment to help reduce the burden and cost of MOC. Pursuit of a legislative resolution was just one of several recommendations from the Association’s MOC Study Committee this year.
If no one was on call…the Board of Medical Scholarship Awards could have seen its funding reduced but instead, the program retained its funding level of $1.4 million for 2019. The BMSA grants medical school loans to medical students and accepts as payment for the loan that student’s locating to a rural area to practice medicine. The BMSA is a critical tool for recruiting medical students to commit to practice in rural areas. As well, the economic footprint of every physician is at least $1 million, which improves both community health and local economies.
If no one was on call…Medicaid cuts could have been severe, possibly reducing access for patients within an already fragile system in which less than 20 percent of Alabama physicians participate. The 2019 budget has sufficient funds available for Medicaid without scheduled cuts to physicians. However, increasing Medicaid reimbursements to Medicare levels could further increase access to care for Medicaid patients and remains a Medical Association priority.
Beating Back the Lawsuit Industry
While Alabama’s medical liability laws have fostered fairness in the courtroom and improved the legal climate, each year personal injury attorneys seek to undo parts of the very law that helps keep “jackpot justice” and frivolous suits in check.
If no one was on call…bill language that could have pulled physicians into new lawsuits targeting opioid drug makers and opioid wholesale drug distributors could have been included in the final version of the legislation, whose subject matter was originally limited to placing new criminal penalties on unlawful possession, distribution and trafficking of Fentanyl. After the liability language was added on the House floor, a committee of the House and Senate removed the new cause of action language that could have affected physicians. Additionally, an unsuccessful attempt was made to amend this same bill to give law enforcement the authority to determine what is the unlawful “prescribing” or “dispensing” of prescription drugs. The final bill that passed contained neither of these elements that would have been problematic for physicians.
If no one was on call…physicians and medical practices could have been forced to provide warranty and replacement coverage for “assistive medical devices.” As originally drafted in the bill, the term “assistive medical devices” was broadly defined to include any device that improves a person’s quality of life including those implanted, sold or furnished by physicians and medical practices like joint or cochlear implants, pacemakers, hearing aids, etc. However, the Medical Association successfully sought an amendment to remove physicians, their staff and medical practices from having any new warranty or assistive device replacement responsibility under the act, and the final version doesn’t expand liability on doctors.
If no one was on call…legislation granting nurse practitioners and nurse midwives new signature authority outside of a collaborative practice and for some items prohibited under federal law – thereby significantly expanding liability for collaborating physicians – could have become law. The Medical Association successfully sought to ensure that all new signature authority granted to CRNPs and CNMs was subject to an active collaborative agreement and all additional forms or authorizations granted were consistent with federal law, protecting collaborating physicians from new liability exposure. The final bill was favorably amended with this language.
If no one was on call…physicians could have been held legally responsible for others’ mistakes including individuals following or failing to follow DNR orders on minors. The language of the final bill does not expand liability for physicians.
Protecting Public Health and Access to Quality Care
Every session, various pieces of legislation aimed at improving the health of Alabamians are proposed. At the same time however, many bills are also introduced that endanger public health and safety, like those where the Legislature attempts to set standards for medical care, which force physicians and their staffs to adhere to non-medically established criteria, wasting health care dollars, wasting patients’ and physicians’ time and exposing physicians to new liability concerns.
If no one was on call…collaborative practice in Alabama between nurse practitioners, nurse midwives and physicians could have been abolished. The legislation did not pass. Read the joint statement on the bill from the Medical Association and allied medical specialties here. The bill may return next session.
If no one was on call…legislation to give law enforcement the authority to determine what is the unlawful “prescribing” or “dispensing” of controlled substances (and making violations a Class B Felony) could have become law. The Medical Association sought changes to the bill to require prosecutors to have to prove beyond a reasonable doubt that a physician knowingly or intentionally prescribed controlled substances for other than a legitimate medical purpose and outside the usual course of his or her professional practice, and also to ensure sufficient qualifications for expert witnesses. The sponsor however – arguing that expert witness testimony for prosecuting a physician should not be required – asked the bill not be passed and instead “indefinitely postponed it,” killing the bill for the 2018 session. The bill will return next session.
If no one was on call…marriage and family therapists could have been allowed unprecedented authority to diagnose and treat mental illnesses without restriction. The legislation would also have deleted numerous prohibitions in current law including prescribing drugs, using electroconvulsive therapy, admitting to a hospital and treating inpatients without medical supervision, among other things. The Medical Association offered a substitute bill that (1) ensures all diagnoses and treatment plans made by MFTs are within the MFT treatment context; (2) ensures MFTs cannot practice outside the boundaries of MFT services; (3) prohibits MFTs from practicing medicine; and, (4) ensures all the current prohibitions in state law regarding prescribing of drugs, electroconvulsive therapy and inpatient treatment remain intact. The final bill that is now law contains all of these elements.
If no one was on call…legislation creating a new state board with unprecedented authority over medical imaging could have passed. The legislation would have required x-ray operators, magnetic resonance technologists, nuclear medicine technologists, radiation therapists, radiographers and radiologist assistants to acquire a new license from a new state board, a board granted total control over the scope of practice for each licensee. Quality and access to care concerns abounded with this legislation that many saw as unnecessary. The legislation did not pass, but is likely to return next session.
If no one was on call…proposals to move the PDMP away from the Alabama Department of Public Health and instead under the authority of some other state agency or even to a private non-profit organization could have been successful. In working with the Governor’s Opioid Task Force, the Medical Association stressed the Health Department was the proper home for the PDMP and the Task Force did not recommend that the PDMP be moved elsewhere.
If no one was on call…legislation to place new requirements on and increase civil liability exposure on referring physicians under the Women’s Right to Know Act could have become law. The legislation aimed to provide a woman seeking an abortion with notice that she can change her mind at any time and be entitled to a full refund for not going through with the abortion. The Medical Association sought to fix a longstanding problem that places information-provision requirements on referring physicians under the Women’s Right to Know law. While the Association’s language was adopted, the bill failed to pass. The bill is expected to return next session.
If no one was on call…state law could have been changed to require mandatory PDMP checks on every prescription. Attempts to change this are expected in 2019.
If no one was on call…law enforcement could have been granted unfettered access to the prescriptions records of all Alabamians. Attempts to change this are expected in 2019.
Other Bills of Interest
Rural physician tax credits…legislation to increase rural physician tax credits and thereby increase access to care for rural Alabamians did not pass but will be reintroduced next session.
Infectious Disease Elimination…legislation to establish infectious disease elimination pilot programs to mitigate the spread of certain diseases failed to garner enough support to pass this session.
Data breach notification…relating to consumer protection, is known as the “data breach bill.” In the event of a data breach by a HIPAA-covered entity, as long as the entity follows HIPAA guidelines for data breaches and notifies the attorney general if the breach affects more than 1,000 people, the HIPAA-covered entity is exempt from any penalties. Now, only North Dakota lacks a “data breach” notification statute. The bill was signed by the Governor.
School-based vaccine program…a Senate Joint Resolution urging the State Department of Education and the Alabama Department of Public Health to encourage all schools to participate in a school-based vaccine program passed in 2018. The Medical Association, Alabama Academy of Pediatrics and Alabama Academy of Family Physicians issued a joint statement in opposition to the resolution.
“While we remain committed to increasing vaccine rates in Alabama for the very reasons outlined in the “Whereases” of the resolution, we are very concerned about the potential disruption that a widespread school-based program could bring to local practices and the likelihood of detrimental effects of adolescents not visiting the doctor-their medical home–during the critical teen years,” the joint statement from the medical societies reads.
While Gov. Ivey did not sign the resolution, it was ratified under state law without her signature.
Workers comp…legislation to penalize an individual from obtaining workers comp benefits by fraudulent means was introduced this session. The Medical Association successfully sought an amendment to require notice to the physician of termination of a worker’s benefits and to ensure continued payment of claims submitted by a physician until that notice is received. The bill failed to see any action this session.
Genital mutilation…legislation criminalizing the genital mutilation of a minor female was introduced this session. The Medical Association successfully sought an amendment to exclude emergency situations and procedures. The bill died in the Senate during the last days of the session. It is expected to return next year.
If the Medical Association was not on call at the Legislature, countless bills expanding doctors’ liability, placing standards of care into state law, lowering the quality of care provided and diminishing the practice of medicine could have passed. At the same time, positive strides in public health – like new funding for a much-needed PDMP upgrade, better data-sharing with VA facilities and the resolution on MOC – would not have occurred. The Medical Association is Alabama physicians’ greatest resource in advocating for the practice of medicine and the patients they serve.
Questions? For more information contact Niko Corley at ncorley@alamedical.org –
Tags: adph, breach, civil, collaborative, comp, coverage, data, disease, dnr, drug, epidemic, genital, image, imagine, infectious, legislative, liability, Medicaid, midwife, midwives, mutilation, nurse, PDMP, physician, prescribe, rural, scholarship, therapist, unlawful, VA, vaccine, worker
Posted in: Advocacy




![What If No One Was On Call [at the Legislature]?](https://alabamamedicine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/AlabamaStateHouse_banner-620x161.jpg)






