This is the second in a series of articles reviewing notable changes in the 2019 Physician Fee Schedule Final Rule and provides a deeper discussion of the potential changes to the E/M Coding regime scheduled to take effect in 2021. For the original article, please see Evaluating and Managing the E/M Codes for 2019 and Beyond.
Brief Recap
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services proposed some major changes to the way Evaluation and Management services are reimbursed in the 2019 Physician Fee Schedule Proposed Rule. The PFS Final Rule[1] adopted some of the proposed changes but scheduled them to take effect in 2021. The commentary on these proposals and CMS’s responses in the PFS Final Rule provide some valuable insight into what CMS is trying to accomplish with the E/M reimbursement changes and what these changes might ultimately look like when made effective in 2021.
Proposals for 2021
Collapsing Reimbursement for Levels 2-4. CMS has proposed to collapse the reimbursement for E/M level 2 through level 4[2] codes into a single reimbursement amount for office/outpatient settings. To come up with this combined payment rate, CMS is taking the average of the current inputs for determining E/M reimbursement (work RVUs, direct PE inputs, time, and specialty mix) for level 2 through 4 E/M codes, weighted by the frequency with which each code is currently billed (based on the most recent five years of utilization data). For an example of what this new reimbursement structure might look like, see Table 19 and Table 20 below (excerpted from the Final Rule), which compare the 2021 E/M reimbursement methodology to the current methodology for both new and established patients in terms of 2018 dollars:
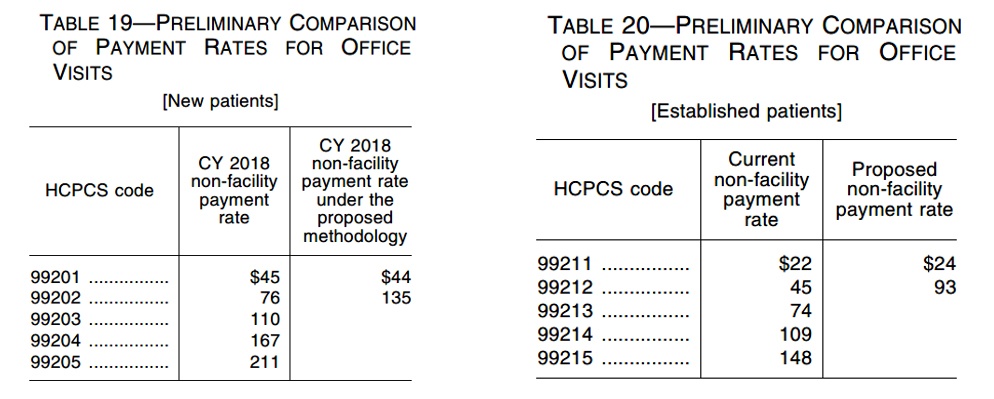 As you might expect, this new reimbursement structure will likely result in a reduction in overall reimbursement for many physicians who ordinarily bill higher level E/M codes. Fortunately, CMS is proposing new add-on codes (to be billed only with the combined level 2 through 4 visits) with additional reimbursement which should mitigate some of the effects of the new E/M reimbursement structure.
As you might expect, this new reimbursement structure will likely result in a reduction in overall reimbursement for many physicians who ordinarily bill higher level E/M codes. Fortunately, CMS is proposing new add-on codes (to be billed only with the combined level 2 through 4 visits) with additional reimbursement which should mitigate some of the effects of the new E/M reimbursement structure.
Add-On Codes. CMS finalized its proposal for new add-on codes to account for primary care and particularly complex visits, as well as extended visits associated with E/M services. CMS indicated that there should not be any additional documentation requirements for these add-on codes (for the most part)[3] and that information already captured on the claim form should suffice to show that the E/M service provided was for primary care.
Primary Care Add-On Code. CMS proposed an add-on code (GPC1X) to be appended to claims for primary care E/M services. Notably, the add-on code only applies to face-to-face time with patients[4], and it cannot be appended to a global procedure code that encompasses E/M services. CMS expects this add-on code to be used predominantly by primary care practitioners (e.g., family medicine, internal medicine, pediatrics, and geriatrics), and in fact, indicated that this add-on code would likely be billed for almost all office/outpatient-based E/M services provided by these practitioners. However, CMS also noted that some specialists also function as primary care practitioners (e.g., OB/GYN or cardiologist) and may be able to utilize this add-on code.
Add-On Code for Specialty Professionals with Large E/M Volume. CMS also proposed an add-on code (GCG0X) for certain specialties which perform mostly high-level (4 or 5) E/M services (rather than procedures) involving “non-procedural approaches to complex conditions that are intrinsically diffuse to multi-organ or neurologic diseases.” CMS originally included certain specialties[5] in the descriptor for this add-on code but has noted that several appropriate specialties[6] were omitted and that the appropriate reporting of this add-on code “should be apparent based on the nature of the clinical issues addressed at the E/M visit, and not limited by the practitioner’s specialty.” CMS also noted that there may be some rare instances where both the primary care add-on code and the specialty professional add-on code could be billed for the same service (provided all the requirements for both codes are met in a single E/M visit).[7]
Extended Visit Add-On Code. There is also an add-on code (GPRO1) to account for additional resources utilized when physicians have extended visits with patients. This code may be billed if the practitioner spends between 34 and 69 minutes (for established patients) or 38 and 89 minutes (for new patients) of face-to-face time with the patient, regardless of which level (2, 3, or 4) E/M code was reported. Providers will have to note the amount of time spent face-to-face with the patient in order to bill for the extended visit code.
Choice of Documentation Method. The current (1995 or 1997) E/M documentation guidelines[8] are based on three factors (all of which must be documented): History or Present Illness, Physical Examination, and Medical Decision Making (MDM). Starting in 2021, practitioners will have the option to document E/M services using any one of the following documentation methods: (1) the current (1995 or 1997) guidelines; (2) MDM only; or (3) time only. If practitioners decide to use the existing guidelines or the MDM-only documentation approach, they would only need documentation consistent with the current level 2 E/M service in order to be reimbursed the combined amount for level 2 through 4 E/M services,[9] or consistent with the level 5 documentation requirements where a level 5 E/M code is billed. For practitioners using time as the documentation method, the practitioner must document face-to-face time personally spent with the patient at least equal to the typical time associated with the applicable level of E/M Code.[10]
Regardless of which documentation method practitioners choose, they must still be diligent in documenting medical necessity, as CMS noted several times in the Final Rule that medical necessity would have to be documented in the record regardless of the documentation method the provider chooses. Based on CMS’s comments in the Final Rule, practitioners may expect additional opportunities to comment on the allowable documentation methods in the coming years before the policy is finalized in 2021.
Conclusion
If these proposals move forward over the next several years, it appears there will be substantial disruption not only in how E/M services are reimbursed, but in how they are documented and billed. It is unclear whether these proposals will achieve CMS’s goal of reducing the administrative burden on practitioners, as the proposals simplify E/M coding in some respects and complicate it in others. Either way, practitioners should have the opportunity over the next two years to continue to comment on these proposals in an effort to have CMS modify or refine them before they go into effect in 2021.
Article contributed by Christopher L. Richard with Gilpin Givhan, PC. Gilpin Givhan, PC, is an official partner with the Medical Association.
[1] CMS-1693-F, available at https://s3.amazonaws.com/public-inspection.federalregister.gov/2018-24170.pdf.
[2] CMS originally proposed to collapse the reimbursement for E/M level 2 through 5 services into a single reimbursement amount but for now has decided to keep a separate reimbursement amount for level 5 E/M services to “better account for the care and needs of particularly complex patients.”
[3] For instances where the billing of the appropriate add-on code is not as readily apparent based on the information on the claim form, practitioners should consider additional documentation in the medical record to support the billing of the add-on codes.
[4] There are already add-on codes for non-face-to-face time, such as CCM and BHI codes.
[5] Endocrinology, rheumatology, hematology/oncology, urology, neurology, OB/GYN, allergy/immunology, otolaryngology, cardiology, or interventional pain management.
[6] Nephrology, psychiatry, pulmonology, infectious disease, and hospice and palliative care medicine.
[7] CMS provides an example of a cardiologist in a rural area who provides care for complex cardiac conditions as well as primary care in his or her clinical practice. If the cardiologist provided both primary care services and specialty cardiology services in a given E/M visit, both GPC1X and GCG0X could be billed for the visit.
[8] 1995 Documentation Guidelines for Evaluation and Management Services, available at https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNEdWebGuide/Downloads/95Docguidelines.pdf; 1997 Guidelines for Evaluation and Management Services, available at https://www.cms.gov/Outreach-and-Education/Medicare-Learning-Network-MLN/MLNEdWebGuide/Downloads/97Docguidelines.pdf.
[9] For example, under the current guidelines, the practitioner must document: (1) a problem-focused history that does not include a review of systems or a past family or social history; (2) a limited examination of the affected body area or organ system; and (3) a straightforward MDM measured by minimal problems, data review, and risk (two of these three). By contrast, a practitioner using the MDM-only method would only have to document straightforward MDM measured by minimal problems, data review and risk (two of these three).
[10] This approach is consistent with the current policy guidelines that time can only be used as the applicable documentation method for E/M codes where counseling and/or coordination of care accounts for more than 50% of the face-to-face time between physician and patient. The typical time associated with a service or procedure is maintained in the AMA CPT codebook.
