When was the last time you reviewed your entity’s Contingency Plan? If it has been awhile, or never, you need to get to work. In light of recent natural disasters and ransomware attacks, the necessity of thorough and documented contingency planning, to include backup and disaster recovery, has become a focus for health care entities.
Pursuant to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) health care entities are required to account for the confidentiality, integrity and accessibility of their electronic protected health information (ePHI). They must consider potential incidents that may affect their information systems like fires, vandalism, malware attacks and tornados. Then they must document their strategy for operation during those events.
Contingency planning should begin with a review of the entity’s Risk Analysis. This document identifies what type of ePHI the entity accesses or maintains, where the data resides, and how the entity handles the data. Afterwards, the entity should begin the process of developing specific Administrative Safeguards.
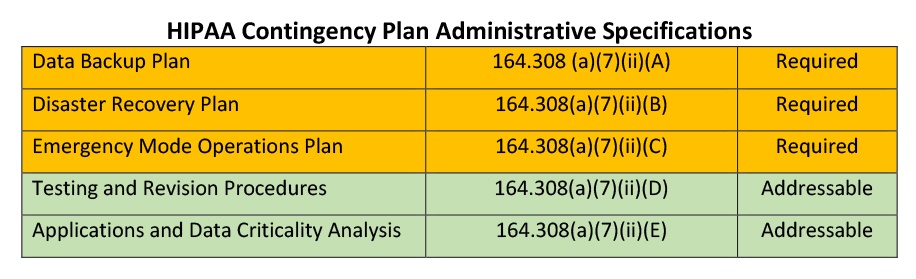
A Data Backup Plan is essential, especially in instances of malware and natural disasters. Entities must put procedures in place to create and maintain exact copy backups of their data that they can readily retrieve. For example, if an entity is heavily damaged by a tornado or fire, they must be able to gain access to the data that they previously utilized within their entity. Without the benefit of timely system backups, the entity would not be able to recover up-to-date data which can be a serious liability when treatment decisions are being made about patients/clients without the benefit of their most current records.
The entity should ensure that there is an appropriate off-site backup of the entity’s ePHI and that the backup is being appropriately performed. These exact copy backups generally occur on a daily, weekly and monthly basis. The entity should maintain copies of these backups and should test the system periodically to ensure that the backup process is working in accordance with the required standards.
The ability to recover lost or stolen data can be critical. The entity should ensure that they have an effective Disaster Recovery Plan that complies with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) specifications.[1] The Disaster Recovery Plan should identify risks observed in the Risk Analysis and reflect a comprehensive plan to recover ePHI within specific time parameters, generally 24 to 48 hours. Additionally, careful consideration must be given to appropriate off-site locations that the entity could utilize if their primary location is no longer available. All workforce members should be informed of the plan and trained on their specific role.
An Emergency Mode Operations Plan documents the manner in which the entity will work throughout the course of the emergency. This relates to the critical business processes that must take place to protect ePHI during and following the emergency or disaster. Examples include determining the need for additional equipment or supplies, ensuring hardware and software compatibility to retrieve ePHI and if necessary, communicating changes to patients/clients.
Testing and Revision Procedures are required for the Data Backup, Disaster Recovery and Emergency Mode Operation Plans. These tests should occur within the timelines listed in the entities Risk Analysis and in all instances no less than annually. The testing process should be documented and evaluated to determine any need for revision.
Entities should perform an Application and Data Criticality Analysis to identify the information systems that are most important from a business operations perspective. This allows the entity to prioritize which databases need to be restored and in what order. For example, if a health care provider were the victim of a ransomware attack and they were attempting to recover the data, the Application and Data Criticality Analysis would identify the exact systems that are most crucial to their operations, allowing them to more easily prioritize the recovery process.
What does a compliance professional look for when auditing an entity for compliance with contingency planning? Entities should be able to produce the following:
- A documented Contingency Plan which covers each of the specifications listed above, namely Data Backup Plan, Disaster Recovery Plan, Emergency Mode Operations Plan, Testing and Revision Procedures and Application and Data Criticality Analysis;
- Documented roles and responsibilities of workforce members during disasters or emergencies;
- Documentation that identifies the entities critical applications;
- Documentation to demonstrate the plan is periodically reviewed and tested; and
- Documentation that reflects whether amendments to the Contingency Plan or Risk Analysis were warranted and implemented, if applicable.
While contingency planning is important for appropriate business operations and HIPAA compliance, it is also critical to patient care. Patients count on health care providers to provide appropriate treatment and care during normal periods and during emergencies. If an emergency or disaster renders an entity without access to their ePHI with no plan to recover or otherwise gain access to the data, that creates unnecessary liability on behalf of the provider for treating the patient without access to their current records. Patient care should be paramount to the mission of all health care entities.
[1] Although only federal agencies are required to follow NIST standards, they represent industry standards for how health care entities should handle ePHI.
Samarria Dunson, J.D., CHC, CHPC is attorney/principal of Dunson Group, LLC, a health care compliance consulting and law firm in Montgomery, Alabama. www.dunsongroup.com
